abstract: Stress reminiscent of intraocular pressure elevation within the eye factors the retinal tissue to bear transcriptional and epigenetic alterations similar to herbal getting old.
supply: UC Irvine
New analysis from the school of California, Irvine, suggests growing older is a vital component of retinal ganglion mobilephone demise in glaucoma, and that novel pathways can be focused when designing new treatments for glaucoma patients.
The look at become posted these days in aging phone. together with her colleagues, Dorota Skowronska‐Krawczyk, Ph.D., assistant professor within the Departments of Physiology & Biophysics and Ophthalmology and the school of the middle for Translational vision research at the UCI school of medication, describes the transcriptional and epigenetic changes happening in aging retina.
The group shows how stress, corresponding to intraocular force (IOP) elevation within the eye, reasons retinal tissue to endure epigenetic and transcriptional changes similar to natural ageing. And, how in young retinal tissue, repetitive stress induces points of accelerated ageing together with the accelerated epigenetic age.
aging is a popular system that influences all cells in an organism. within the eye, it is a major risk aspect for a gaggle of neuropathies called glaucoma. as a result of the enhance in getting older populations worldwide, existing estimates demonstrate that the variety of individuals with glaucoma (aged 40-eighty) will raise to over a hundred and ten million in 2040.
"Our work emphasizes the significance of early diagnosis and prevention in addition to age-certain administration of age-related illnesses, including glaucoma," spoke of Skowronska-Krawczyk.
"The epigenetic alterations we followed indicate that alterations on the chromatin level are got in an accumulative method, following a couple of circumstances of stress. This gives us with a window of opportunity for the prevention of imaginative and prescient loss, if and when the disease is identified early."
In humans, IOP has a circadian rhythm. In healthy people, it oscillates customarily within the 12-21 mmHg range and tends to be maximum in approximately two thirds of people all the way through the nocturnal period.
because of IOP fluctuations, a single IOP size is frequently insufficient to signify the precise pathology and risk of disorder progression in glaucoma sufferers.
long-term IOP fluctuation has been suggested to be a robust predictor for glaucoma development. This new examine suggests that the cumulative impact of the fluctuations of IOP is directly accountable for the getting old of the tissue.
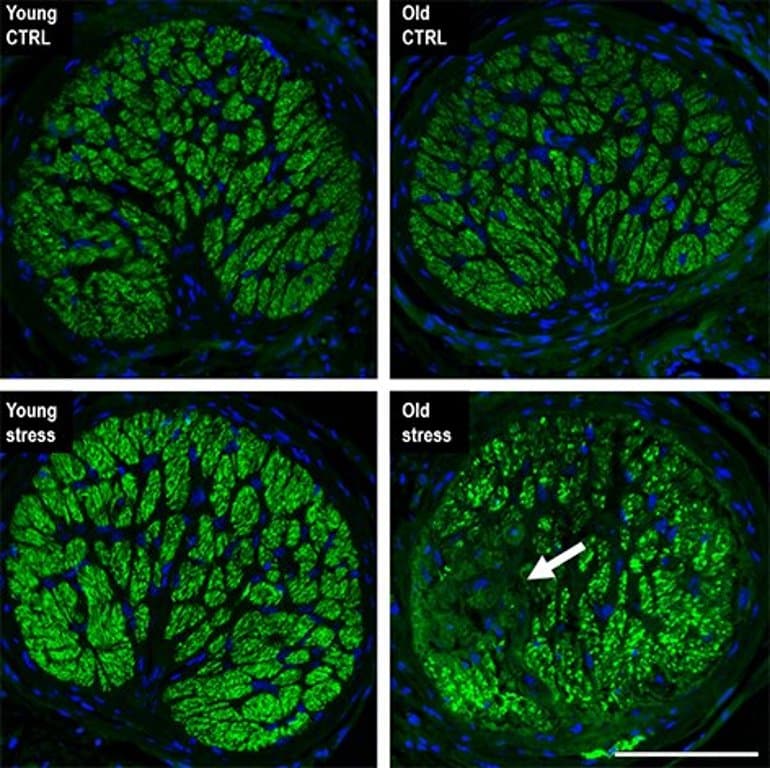 When the UCI-led crew investigated the optic nerve head of eyes treated with mild drive elevation, they cited that within the young optic nerve head, there was no signal of loss of axons. however, within the optic nerves of historical animals, significant sectorial lack of axons become accompanied corresponding to the phenotype generally followed in glaucoma patients. credit: UCI school of drugs
When the UCI-led crew investigated the optic nerve head of eyes treated with mild drive elevation, they cited that within the young optic nerve head, there was no signal of loss of axons. however, within the optic nerves of historical animals, significant sectorial lack of axons become accompanied corresponding to the phenotype generally followed in glaucoma patients. credit: UCI school of drugs "Our work shows that even moderate hydrostatic IOP elevation outcomes in retinal ganglion cell loss and corresponding visual defects when performed on aged animals," pointed out Skowronska-Krawczyk.
"we are carrying on with to work to be mindful the mechanism of accumulative alterations in growing old to be able to locate capabilities pursuits for therapeutics. we are additionally checking out distinct approaches to steer clear of the accelerated getting old manner resulting from stress."
Researchers now have a new device to estimate the influence of stress and medicine on the ageing repute of retinal tissue, which has made these new discoveries viable. In collaboration with the Clock basis and Steve Horvath, Ph.D., from Altos Labs, who pioneered the construction of epigenetic clocks that can measure age according to methylation adjustments in the DNA of tissues, it turned into feasible for researchers to exhibit that repetitive, mild IOP elevation can accelerate epigenetic age of the tissues.
"moreover measuring vision decline and some structural adjustments because of stress and potential remedy, we will now measure the epigenetic age of retinal tissue and use it to discover the top-quality strategy to stay away from vision loss in aging," spoke of Skowronska-Krawczyk.
creator: Press OfficeSource: UC IrvineContact: Press office – UC IrvineImage: The photograph is credited to UC Irvine
common analysis: Open access."Stress brought about growing older in mouse eye" via Qianlan Xu et al. aging mobilephone
summary
Stress induced getting older in mouse eye
getting older, a common manner that influences all cells in an organism, is a tremendous chance ingredient for a group of neuropathies known as glaucoma, the place accelerated intraocular drive is without doubt one of the established stresses affecting the tissue.
Our realizing of molecular affect of ageing on response to stress in retina is awfully restricted; for this reason, we developed a new mouse mannequin to method this query experimentally.
right here we display that susceptibility to response to emphasize increases with age and is primed on chromatin degree.
We display that ocular hypertension activates a stress response this is corresponding to natural getting older and contains activation of inflammation and senescence.
We demonstrate that diverse circumstances of pressure elevation cause growing old of younger retina as measured on transcriptional and DNA methylation stage and are accompanied by native histone amendment adjustments.
Our facts show that repeated stress hastens look of getting older aspects in tissues and imply chromatin modifications as the key molecular components of ageing.
ultimately, our work additional emphasizes the value of early analysis and prevention as well as age-specific administration of age-linked diseases, together with glaucoma.

Post a Comment